Spleen performs multiple functions, although it is not essential for survival ,it is vital for healthy life. Dysfunctions of spleen will produce serious problems.
Tag Archives: health
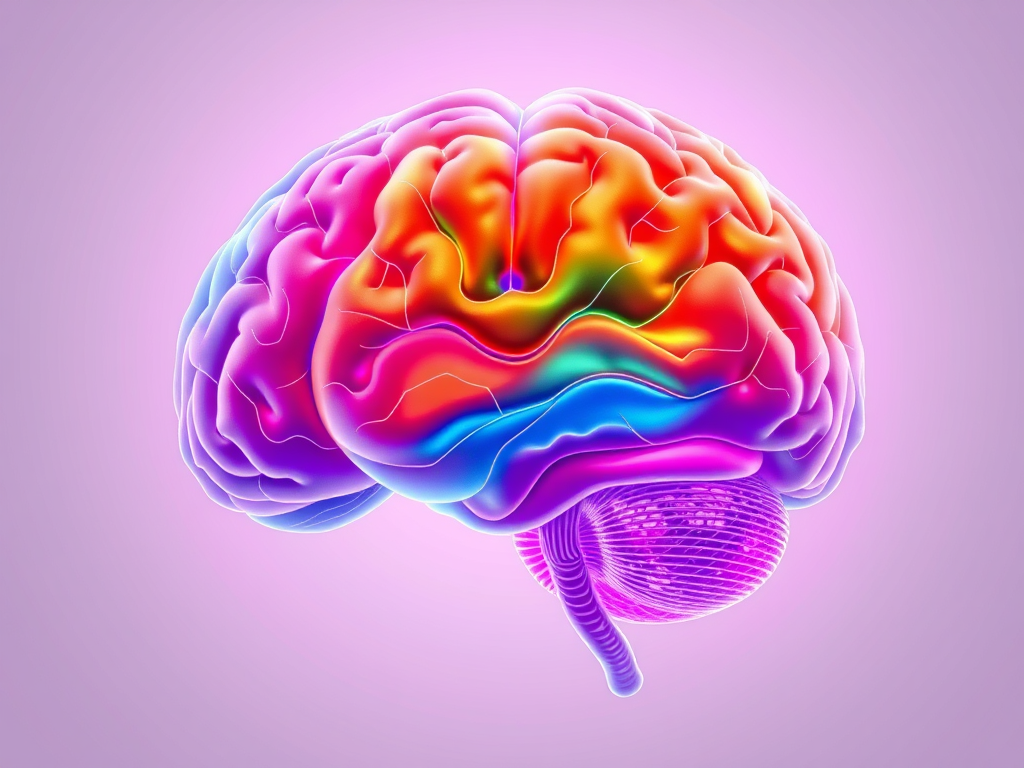
Understanding the Limbic System: Key Functions and Components
1. The limbic lobe and the related subcortical nuclei.
The limbic lobe includes the cingulate gyrus, isthmus, hippocampal gyrus, and uncus.
2. The related subcortical nuclei are the hypothalamus, amygdala, septal nuclei, portion of the basal ganglion,paraolfactory area, and anteriorthalamic nucleus.
The hypothalamus is located in the middle of all these structures and plays a vital role in the limbic system.
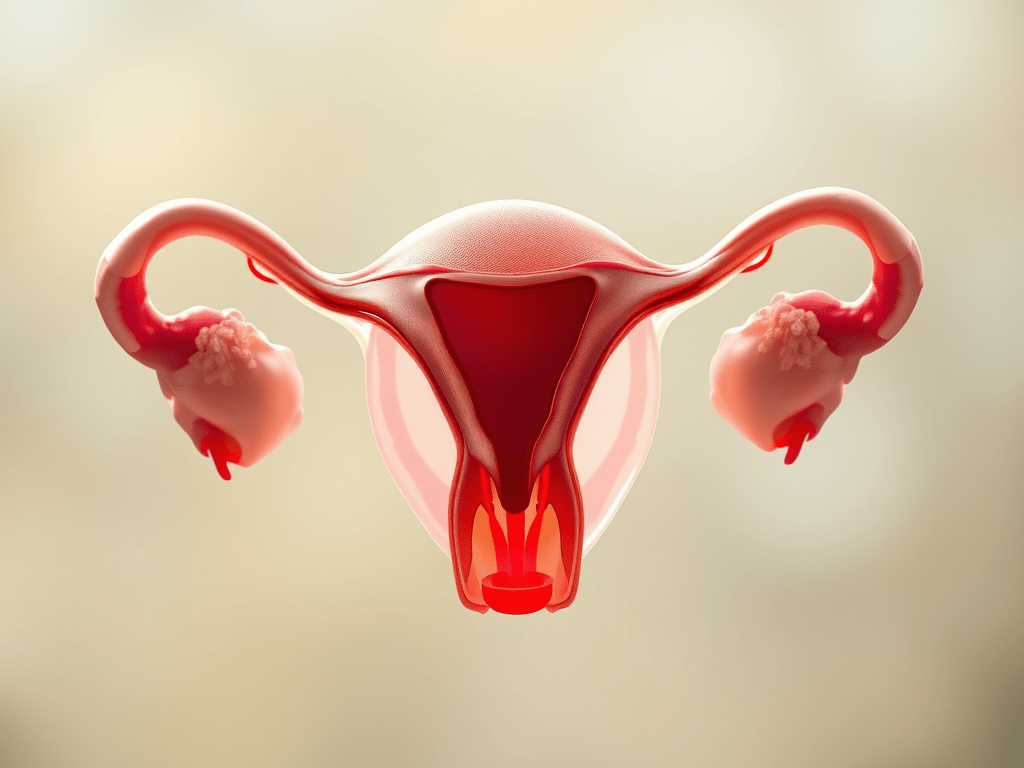
Functions and Structure of the Uterus Explained
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ situated in the female pelvis. It is a pear-shaped (Pyriform) organ that lies between the urinary bladder in front and the rectum behind. The uterus is usually anteflexed and anteverted.
The size of the uterus in an adult female is 3 inches x 2 inches x 1 inch (7.5 cm long x 5 cm wide x 2.5 cm thick. The weight of the adult nulliparous uterus ranges from 50 to 80 g.
The uterus develops from the fused vertical part of the two Müllerian ducts.
Neuroendocrine Reflex Explained: Homeostasis and Examples
The neuroendocrine reflex integrates two systems of the body that are responsible for maintaining homeostasis. The two systems are the nervous and endocrine systems. They affect each other through both negative and positive feedback mechanisms to regulate the body’s overall functions. The internal and external stimuli stimulate them.
Understanding Kidney Structure and Functions
The kidney is a vital organ that performs many functions, including the excretion of metabolic waste, maintaining homeostatic balance, regulating body fluid volume, controlling electrolyte concentration in body fluids, and regulating acid-base balance, as well as endocrine and metabolic functions.
Why Anatomy is Essential for Medical Professionals
Human anatomy is a branch of science that explains the structure of the human body. In human anatomy, we study the macroscopic and microscopic structures of the human body, how it is formed, and how these structures work synergistically.
Normal Range and Factors Affecting Cardiac Output
Cardiac output is the blood volume pumped from each ventricle per minute, expressed in liters /per minute .Cardiac output is an essential parameter in hemodynamics, the study of blood flow. Its importance is globally accepted.
Understanding Human Physiology: Past, Present, and Future
The study of human physiology has been ongoing for time immemorial. The first authentic available record is found in the Sushruta Samhita and Charak Samhita, dating back to around 600 BCE. They proposed that vata, pitta, and kapha regulate the body’s functions.
Bile: Formation, Functions, and Health Implications
Bile is a physiological fluid that is dark green to yellowish-brown in color and produced by the liver.
In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver and drained by bile canaliculi to the right and left hepatic ducts. The right and left hepatic ducts join to form the common hepatic duct. The cystic duct from the gall bladder joins the common hepatic duct and forms the common bile duct.
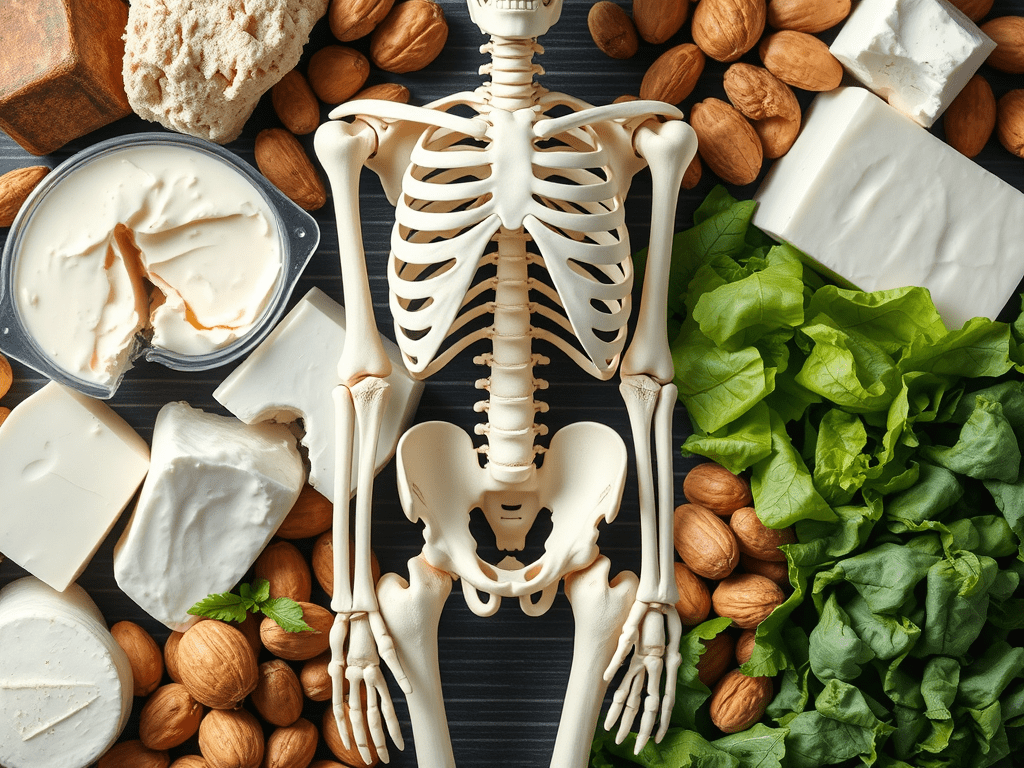
Understanding Calcium: Benefits and Functions in the Body
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body. The amount of total body calcium ranges from 1100 to 1200 g, out of which 99% is present in the skeleton, and the remaining 1% is in the tissue and body fluids.